For a long time, webmasters viewed an SSL certificate as simply nice to have. However, it offers more advantages than you might think.
Since Google declared “https” a ranking factor in August 2014, website operators should be informing themselves whether encryption is appropriate for their websites or not. Since January 1, 2017, secure connections can also be seen in the SERPs through the addition of “https” before the URL. But, there are still numerous websites without SSL encryption. In this article, we will show you how you can establish an SSL certificate for your website and what you should pay attention to in the process.
What Happens with SSL Encryption?
When a website is secured through SSL, the connections between a client and the server are encrypted. Visitors can therefore open your website securely with their browser and can, for example, enter data for their order without this being seen and read by third parties. So that a secure connection can be created between browser and server, the browser asks the server whether it belongs to the called-up domain. In order to confirm this connection, an SSL certificate is required, which provides a type of proof of legitimacy for the website.
The required SSL certificate is awarded by “certification authorities” (CA). If the SSL certificate is issued for a publicly accessible website, the corresponding CA first checks all the information on this site. The certificate can then be viewed publicly and is filed with the CA. To create the encryption, the public key is first used to secure the transferred information. The data is then encrypted with a second key, which is filed with the certified server.
Choose the Correct SSL Certificate
There are various suppliers of SSL certificates authorized by the CA Security Council. CASC is an interest group that wants to increase security on the internet. Known suppliers of SSL certificates are, for example, GlobalSign, Geo Trust, Symantec, or AlphaSSL as well as Thawte.
In choosing the correct SSL certificate, it is important to determine whether the protected domain should be publicly accessible or not. Public SSL certificates can only be created for public domains, because the certification authorities cannot always identify the ownership of private servers or an intranet. For this reason, the following points mainly involve the SSL certificate of publicly-used internet sites.
SSL certificates are available in various levels of trust. Thus, how much information a transferred file contains and how strongly this is protected plays a role.
There are fundamentally three different SSL certificates available:
1. Extended Validation (EV) – the highest level of encryption
2. Organization Validated (OV) – a medium level of encryption
3. Domain Validated (DV) – the lowest level of encryption
If you don’t want to use a certificate, you should firstly ask yourself how much security you would like to offer your visitors. Also, think about how strong your brand has been in the past. If your brand is connected with a certificate, all domains published under the brand are protected.
1. Extended Validation or EV Certificate
To obtain this certificate, the issuing authorities request a large amount of information. The criteria are considered to be the strictest that must be met to receive SSL encryption. Not only one individual page is certified, but the entire company.
With the EV certificate, visitors can be secure in the knowledge that your website is operated by your company, and that the connections with this domain are secure.
2. Organization Validated or OV Certificate
This SSL certificate also contains an authorization of your company. To receive this certificate, the respective company checks data which is prepared by you. But, your information is not so strongly emphasized as with numerous other EV certificates. If visitors want to see this data, they have to call up individual details separately.
3. Domain Validated or DV Certificate
A DV certificate likewise encrypts your website through SSL. How, this certificate contains a lot less data about you and your company. The DV certificate merely confirms that you are the owner of the website and that you actively manage the site. However, such a certificate does not confirm that it is issued specially for your company, or that your site is actually operated by your company. Therefore, for online shops or other commercially-operated websites, it is recommended to use at least the OV certificate.
One Domain or More?
In the next step, you should check whether you need SSL protection for only one domain, or for an entire series of domains. If you want to secure only one domain, you need an individual domain or “standard certificate.” Here, you can choose between three levels of authentication.
If several domains or sub-domains are to be secured by SSL, you can choose a multi-domain or wild-card certificate. Initially, the costs are clearly higher than for an individual certificate, but, in total, it is more inexpensive to protect several domains with a multi-domain version. The certificate for several domains is also a “subject-alternative-names certificate,” called an SAN certificate for short.
Incorporate the SSL Certificate
If you have obtained an SSL certificate from a supplier, in general, you will receive instructions regarding how to implement it. But the steps are always similar:
- Install the SSL certificate on your server. If you are not using a dedicated server, some web hosts offer an SSL solution with just a few clicks. How the SSL certificate is to be implemented depends on your type of server. Here, you will find a good overview about the installation of the SSL certificate on various servers such as Apache or Exchange:
- Then, choose which sites, sub-domains, or domains should be protected with the certificate.
- Open your sites with various browsers. Let this show you whether elements can be loaded without SSL encryption. With an SSL checker, such as from sslshopper.com, you can check whether your SSL connection is correctly implemented for free.
Checklist – Pay Attention to the Following Six Points
- ✓ After the installation of the SSL certificate, consider setting up a 301 redirect from your website with http to https
You will therefore stop Google from indexing both versions. With duplicate content, the Googlebot doesn’t know which version should be favored. Ultimately, this can hurt the rankings of both versions.
- ✓ File your https domain in the Google Search Console
You will therefore ensure that Google correctly transmits data such as clicks or errors to your website. To do this, log into the search console with your Google account. Then click on the red button “Add property.” Now, enter the site newly encrypted with https into the slot; in the end, you only have to confirm the site. To do this, there are various options available. The simplest is confirming with the Google Analytics account. If you have implemented the tracking code from Google Analytics, you can confirm with just one click.
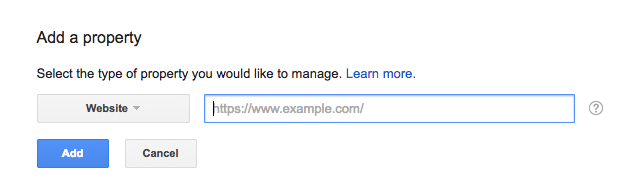
Figure 1: File the website in the Google Search Console.
- ✓ File the https site in your web analysis tool
So that the tracking of your website functions correctly, you should enter the adjustment in the Google Analytics protocol and other web analysis tools.
Under Google Analytics, click on the “Admin” button (bottom left). There, you can change the website protocol with just one click.
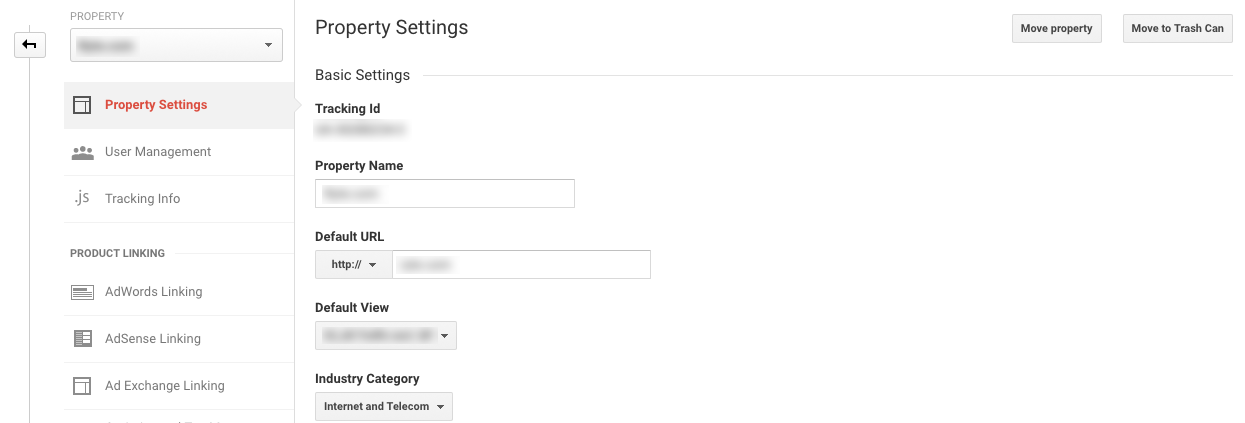
Figure 2: Adjust to https with Google Analytics.
- ✓ Adjust links internally and place https in front so that the connections are secure
- ✓ Correct links to your domain stored in AdWords or other advertising programs
In the Google AdWords administration interface, you can search according to Ad groups. There, you have the opportunity to adjust the log for the link to your web offer to https. In adjusting the link, also consider the AdWords expansions such as site links that offer URLs.
If you are using Google Shopping Ads, you should also change your address in the Google Merchant Center. Consider that the links to your products transmitted in the CSD file are likewise encrypted through https.
- ✓ Also file the https domain with social network profiles such as Facebook or Twitter
To do this, log into the corresponding profile and change the protocol.
Cost and Length of SSL Certificates
All SSL certificates are issued only for a certain time frame. In general, the available time frames last between one and five years. The payment for an SSL certificate is always settled in advance for the entire length.
Simple DL certificates are available for substantially less than $100 per year. If there is a multi-domain SSL certificate or a product with wildcards, the fees can amount to more than $1,000 per year. Prices vary from supplier to supplier, and it pays to compare the costs before booking a certificate. There are also free suppliers, such as letsencrypt.org.
Once you have decided on a certificate, it’s usually easiest to just extend the time frame, but you can also switch to another provider or certificate. This can be sensible, for example, if you take up a new site into your portfolio and if you want to change a certificate for one domain to a multi-certificate.
In making the change, also consider that checking your site can take several days. Your site is also checked in case of an extension. You should, therefore, ideally apply for an extension at least 30 days before the expiration of the certificate, or alternately apply for a new certificate. In this way, you will avoid a double booking of certificates and will avoid having to pay twice, because an SSL certificate must always be paid for at least 12 months in advance.
[kc_row use_container=”yes” _id=”860821″][kc_column width=”12/12″ video_mute=”no” _id=”236575″][crum_title title=”Read Also” _id=”964231″ type=”h1″ inline_link=”yes” title_link=”http://digiprad.com/search-engine-blog/|Search Engine Blog|” css_custom=”{`kc-css`:{`any`:{`box-style`:{`text-align|`:`center`}}}}”][kc_row_inner column_align=”middle” video_mute=”no” _id=”591317″][kc_column_inner width=”100%” _id=”939787″][crum_post_slider layout=”portfolio” number_of_items=”3″ dots=”yes” autoscroll=”yes” time=”5″ number_post=”9″ _id=”214799″ dots_position=”top” post_taxonomy=”post:search-engine-blog” order_by=”ID” order_list=”ASC”][/kc_column_inner][/kc_row_inner][/kc_column][/kc_row]
Conclusion
Today, an SSL certificate is elementary to building the trust of customers and visitors, as well as with Google. It is therefore even more important that your site is secured with SSL. For small blogs without contact forms or shopping carts, in general, a simple certificate is sufficient. If, however, you want to secure a web shop or operate several commercial websites, a multi-domain certificate or an EV certificate is certainly the best solution. In all cases, it is important that after the adjustment of your website to https, you set up redirects in order to avoid duplicate content. Even the great ones of our time have understood the importance of a secure website.
[crum_call_to_action layout=”center” title=”Tell Us About Your Project” desc=”Q2hhdCB3aXRoIHVzIG9uIHdoYXRzYXBw” show_link=”yes” btn_size=”large” _id=”953311″ link=”https://api.whatsapp.com/send?phone=2349067688122|We are online|_blank” btn_color=”primary” css_custom=”{`kc-css`:{`any`:{`title`:{`color|.heading-title`:`#ffffff`},`sub-title`:{`color|.heading-text`:`#ffffff`}}}}”]